Introduction
In the field of precision measurement and instrumentation, understanding the tools and technologies that facilitate accurate data collection is crucial. Among the essential components in this domain are load cells and strain gauges. These devices are pivotal in various industries, from manufacturing and construction to research and development. eTAZ Systems, a leader in innovative measurement solutions, provides advanced products that harness the power of both load cells and strain gauges. This article delves into the fundamental differences, applications, and advantages of load cells and strain gauges, highlighting how eTAZ Systems leverages these technologies to deliver superior performance and accuracy.
What are Load Cells?
Definition and Working Principle
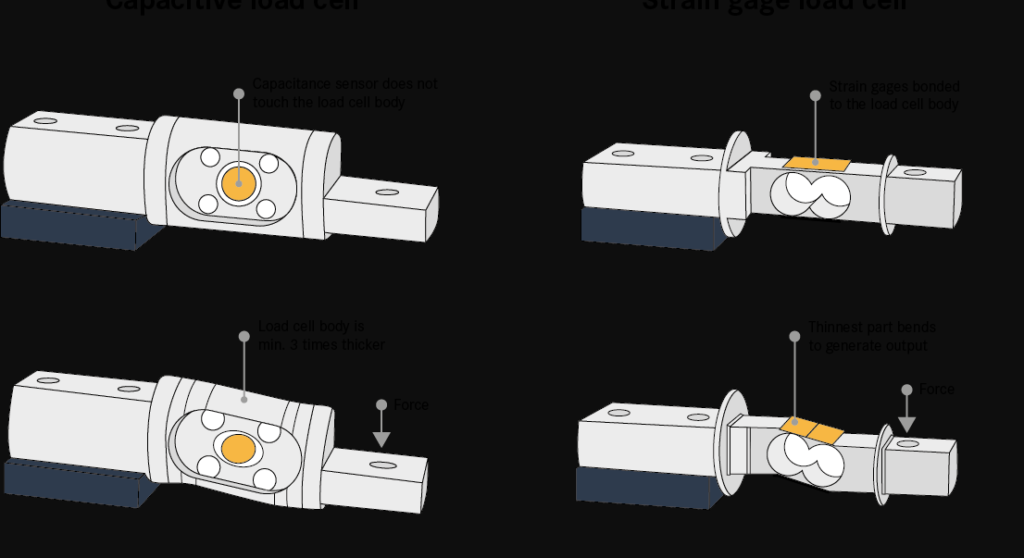
This conversion occurs through a mechanical deformation within the load cell, which is then measured by the change in electrical resistance. Typically, load cells use strain gauges as the primary sensing element. The strain gauges are bonded to a structural member within the load cell, and as this member deforms under load, the strain gauges experience a change in resistance proportional to the applied force.
Types of Load Cells
Load cells come in various types, each suited to specific applications:
- Hydraulic Load Cells: Utilize fluid pressure to measure force.
- Pneumatic Load Cells: Use air pressure for force measurement.
- Strain Gauge Load Cells: The most common type, employing strain gauges to detect deformation.
- Capacitive Load Cells: Measure changes in electrical capacitance caused by deformation.
- Piezoelectric Load Cells: Use piezoelectric materials to generate a charge in response to mechanical stress.
Applications of Load Cells
Load cells are integral to numerous industries and applications:
- Weighing Systems: From retail scales to large industrial scales, load cells ensure precise weight measurements.
- Material Testing Machines: Used to assess the strength and durability of materials.
- Industrial Automation: Monitor and control manufacturing processes.
- Safety Systems: In structures like bridges and buildings to monitor loads and ensure safety.
- Medical Devices: For precise force measurement in various medical applications.
What are Strain Gauges?
Definition and Working Principle
A strain gauge is a sensor whose resistance varies with applied force; essentially, it measures the strain (deformation) in an object. Strain gauges operate on the principle that a conductor’s resistance changes with deformation. When a strain gauge is stretched, its resistance increases; when compressed, its resistance decreases. This change in resistance is proportional to the strain experienced by the material to which the strain gauge is attached.
Types of Strain Gauges
Strain gauges come in several forms, including:
- Foil Strain Gauges: The most common type, made of a metallic foil pattern.
- Wire Strain Gauges: Consist of a length of wire arranged in a grid pattern.
- Semiconductor Strain Gauges: Use silicon or other semiconductor materials, offering higher sensitivity.
- Optical Fiber Strain Gauges: Use changes in light properties within an optical fiber to measure strain.
Applications of Strain Gauges
Strain gauges are used in a wide range of applications:
- Structural Health Monitoring: In buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure to detect stress and potential failure points.
- Aerospace Engineering: To measure strain in aircraft components and ensure structural integrity.
- Automotive Testing: For testing vehicle components and ensuring performance and safety.
- Biomedical Devices: In prosthetics and medical implants to monitor stress and strain.
- Research and Development: For experimental stress analysis and material testing.
Load Cell vs. Strain Gauge: Key Differences

Measurement Focus
- Load Cells: Primarily designed to measure force or weight. They integrate strain gauges but focus on providing a comprehensive measurement of load.
- Strain Gauges: Measure strain, which can then be used to infer force or other mechanical properties when combined with knowledge of the material’s characteristics.
Integration and Complexity
- Load Cells: Generally more complex, incorporating strain gauges within a mechanical structure designed to distribute and measure force. They often include temperature compensation and other features to enhance accuracy.
- Strain Gauges: Simpler devices that can be attached to various structures to measure strain. They require additional circuitry and calibration to convert strain measurements into meaningful data like force or stress.
Accuracy and Precision
- Load Cells: Typically offer higher accuracy and precision in force measurement because they are specifically designed and calibrated for this purpose.
- Strain Gauges: While highly accurate in measuring strain, converting this data into precise force measurements can be more challenging and dependent on calibration and environmental conditions.
Application Scope
- Load Cells: Used in applications where direct force measurement is essential, such as weighing systems, material testing, and industrial automation.
- Strain Gauges: Employed in applications requiring detailed analysis of strain patterns, structural health monitoring, and experimental stress analysis.
eTAZ Systems: Harnessing the Power of Both Technologies
eTAZ Systems stands at the forefront of measurement technology, offering products that leverage both load cells and strain gauges to meet diverse industry needs. Their innovative solutions provide unparalleled accuracy, reliability, and versatility.
Advanced Load Cells
eTAZ Systems’ load cells are designed with precision and durability in mind. Key features include:
- High Accuracy: Utilizing advanced strain gauge technology and meticulous calibration processes.
- Robust Construction: Built to withstand harsh industrial environments and heavy loads.
- Versatile Designs: Available in various configurations to suit different applications, from small-scale precision measurements to large-scale industrial weighing.
Cutting-Edge Strain Gauges
eTAZ Systems offers state-of-the-art strain gauges that provide high sensitivity and reliability. Highlights include:
- Enhanced Sensitivity: Using semiconductor materials for higher gauge factors and better resolution.
- Durability: Designed to operate reliably in extreme conditions, including high temperatures and corrosive environments.
- Flexible Integration: Can be used in diverse applications, from aerospace and automotive testing to biomedical devices and structural health monitoring.
Integrated Systems
eTAZ Systems excels in creating integrated measurement solutions that combine load cells and strain gauges. These systems offer comprehensive monitoring and control capabilities, essential for complex applications such as:
- Smart Infrastructure: Combining load cells and strain gauges for real-time monitoring of buildings, bridges, and other critical structures.
- Industrial Automation: Enhancing manufacturing processes with precise force and strain measurements to improve quality control and efficiency.
- Research and Development: Providing researchers with detailed insights into material behavior and structural performance.
Advantages of eTAZ Systems’ Solutions
Precision and Reliability
eTAZ Systems’ commitment to precision and reliability ensures that their load cells and strain gauges deliver accurate and consistent measurements. This is achieved through rigorous quality control, advanced materials, and state-of-the-art manufacturing processes.
Customization and Flexibility
Understanding that each application has unique requirements, eTAZ Systems offers customizable solutions. Whether it’s a specific load cell configuration or a specialized strain gauge design, their team works closely with clients to develop tailored solutions.
Comprehensive Support
From initial consultation to ongoing technical support, eTAZ Systems provides comprehensive service to ensure optimal performance of their measurement solutions. Their expertise helps clients navigate complex measurement challenges and achieve their goals efficiently.
Case Studies: eTAZ Systems in Action
Case Study 1: Structural Health Monitoring
Challenge: A major bridge required continuous monitoring to ensure safety and longevity.
Solution: eTAZ Systems provided an integrated system combining load cells and strain gauges. This setup enabled real-time monitoring of stress and load distribution across the bridge, allowing for early detection of potential issues.
Outcome: Enhanced safety and extended lifespan of the bridge through proactive maintenance and timely interventions.
Case Study 2: Industrial Automation
Challenge: A manufacturing plant needed to improve quality control and efficiency in its production line.
Solution: eTAZ Systems implemented load cells in the assembly line to monitor forces during critical processes. Strain gauges were used to analyze strain patterns in machine components, ensuring optimal performance.
Outcome: Significant improvement in product quality and manufacturing efficiency, leading to increased customer satisfaction and reduced operational costs.
Case Study 3: Biomedical Device Development
Challenge: A medical device company required precise force measurement in the development of a new prosthetic limb.
Solution: eTAZ Systems provided high-precision load cells and strain gauges tailored to the specific requirements of the prosthetic device. This allowed for accurate measurement of forces and stresses during testing.
Outcome: Successful development of a highly functional and reliable prosthetic limb, improving the quality of life for end-users.
Future Trends and Innovations
eTAZ Systems is continually pushing the boundaries of measurement technology. Future trends and innovations include:
Smart Load Cells and Strain Gauges
Integration of IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities to create smart sensors that offer real-time data analysis and remote monitoring. These advancements will enable more efficient and proactive maintenance strategies.
Advanced Materials
Development of new materials with superior properties for strain gauges and load cells, enhancing their performance and durability in extreme conditions.
Enhanced Data Analytics
Leveraging big data and machine learning to provide deeper insights and predictive analytics, helping industries to optimize processes and improve decision-making.
Conclusion
Load cells and strain gauges are indispensable tools in the realm of precise measurement and instrumentation. Through the innovative solutions offered by eTAZ Systems, industries can achieve unparalleled accuracy, reliability, and efficiency in their measurement tasks. Whether it’s for structural health monitoring, industrial automation, or cutting-edge research and development, eTAZ Systems’ load cells and strain gauges provide the foundation for success. As technology continues to evolve, eTAZ Systems