Displacement transducers are vital in industries that require precise measurement of linear or angular displacement eTAZ systems They convert the movement or position of an object into an electrical signal, which can then be processed, displayed, or used to control other systems. This article provides a detailed overview of displacement transducers, their design considerations, the services offered around them, and answers to frequently asked questions (FAQs).
Displacement Transducers
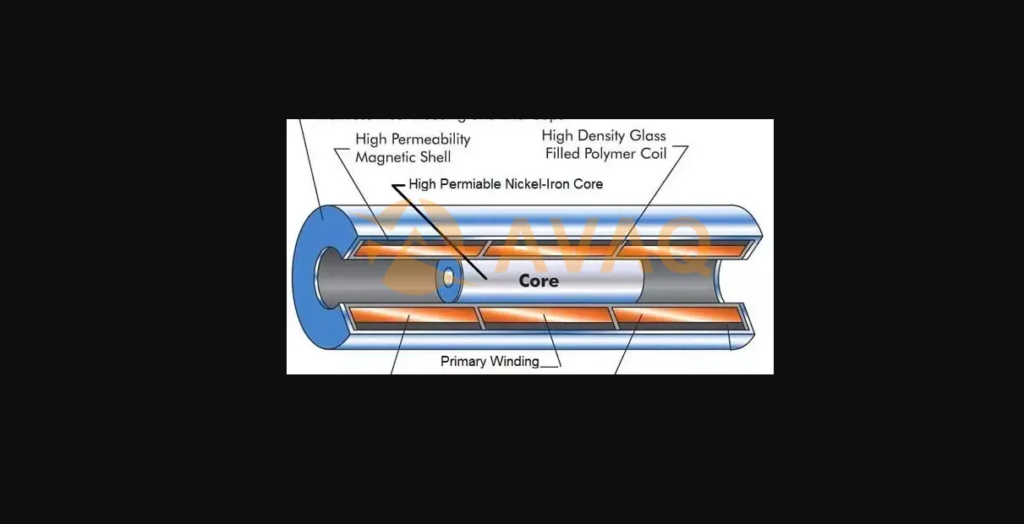
“A displacement transducer measures the movement of an object. There are several Services types of displacement transducers, each suited to specific applications:
Linear Variable Differential Transformers (LVDTs): These are widely used for measuring linear displacement with high accuracy.
Rotary Variable Differential Transformers (RVDTs): These are ideal for measuring angular displacement, particularly in applications requiring rotational position measurement.
Potentiometric Transducers: Utilizing a resistive element to measure displacement, these are simple in design but may wear out over time due to physical contact.
Capacitive and Inductive Transducers: These measure displacement without physical contact, making them ideal for applications where durability is crucial.
Various industries, including automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and robotics, use displacement transducers for precise position measurement.
Design of Displacement Transducers
Designing a displacement transducer involves several important consideration
Accuracy and Precision: The transducer must deliver high accuracy and precision in measurement, especially in fields like aerospace, where even minor errors can be problematic.
Range of Measurement: The design must cater to the required measurement range, from a few millimeters to several meters, depending on the application.
The transducer must endure the environmental conditions it will face, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, or vibration.
Signal Processing: The electrical signal generated by the transducer must be processed accurately, often involving amplification, filtering, or digital conversion.
Mechanical Design: The transducer must be mechanically robust, especially if used in harsh environments or where it may be subject to physical impact.
Displacement Transducer Services
Designing, manufacturing, and integrating displacement transducers require specialized expertise. Companies typically offer several key services in this field:
Custom Design and Development: Many applications need custom-designed displacement transducers tailored to specific needs. This involves close collaboration with clients to develop a transducer that meets their exact requirements.
Calibration and Testing: Calibration ensures the transducer’s accuracy, involving testing under various conditions and making necessary adjustments.
Integration Services: Displacement transducers often need to be integrated into larger systems. This service ensures that the transducer operates seamlessly with other components and systems.
Maintenance and Support: Regular maintenance is essential to keep displacement transducers functioning correctly. Services include regular check-ups, troubleshooting, and repairs if needed.
Training and Consultancy: Companies using displacement transducers can benefit from training on their use and maintenance. Consultancy services can also assist in selecting the right transducer for specific needs.
Applications of Displacement Transducers
Engineers employ displacement transducers in a wide range of applications, such as:
Automotive Industry: Used for measuring the position of components like throttle position sensors and suspension systems.
Aerospace: Crucial for monitoring the position of control surfaces and landing gear.
Manufacturing: Integral to automated machinery for measuring the position of moving parts, ensuring precision in operations like cutting, welding, or assembling.
Robotics: Essential for controlling the movement of robotic arms and other moving parts.
Medical Devices: Used in equipment like MRI machines and surgical robots to ensure precise movement and positioning.
FAQs: Displacement Transducers
Q1: What is a displacement transducer?
A1: A displacement transducer is a sensor that measures the movement or position of an object and converts it into an electrical signal. It can measure either linear or angular displacement, depending on the transducer type.
Q2: What are the different types of displacement transducers?
A2: The main types include Linear Variable Differential Transformers (LVDTs), Rotary Variable Differential Transformers (RVDTs), potentiometric transducers, and capacitive and inductive transducers..
Q3: How do I choose the right displacement transducer for my application?
To determine the choice, consider factors such as the range of displacement to be measured, required accuracy, environmental conditions, and how well the transducer integrates with existing systems. Consulting an expert will help you select the appropriate transducer.
Q4: How accurate are displacement transducers?
A4: The accuracy of a displacement transducer depends on its design and calibration. High-quality transducers can measure displacement with very high accuracy, often within microns for linear transducers and fractions of a degree for rotary transducers.
Q5: Can displacement transducers be used in harsh environments?
“Many manufacturers design displacement transducers to operate in harsh environments. They build these transducers to withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, and vibration based on the application’s requirements.”
Q6: What is the lifespan of a displacement transducer?
A6: The lifespan varies depending on the transducer type and the conditions in which it is used. Contact-based transducers, like potentiometric types, may wear out faster, while non-contact types, like inductive or capacitive transducers, typically last longer.
How does one calibrate a displacement transducer?
A7: Calibration involves comparing the transducer’s output with a known reference standard and making adjustments to ensure accuracy. This process may need to be repeated periodically, especially in environments where conditions can change.
Q8: Can other systems integrate displacement transducers?
A8: Displacement transducers often integrate with larger systems, such as control systems in machinery or data acquisition systems in research. Integration services ensure that the transducer works seamlessly with other components.
Q9: What maintenance do displacement transducers require?
A9: Maintenance typically includes regular inspections, cleaning, and recalibration. For contact-based transducers, checking for wear and tear is essential. Non-contact transducers generally require less maintenance but still need regular check-ups to ensure optimal performance.
Q10: Are displacement transducers expensive?
A10: The cost of a displacement transducer can vary widely depending on the type, accuracy, and range of measurement required. Custom-designed transducers and those used in high-precision applications tend to be more expensive.
Q11: Can medical applications use displacement transducers?
A11: In medical devices where precise movement or positioning is critical, such as in MRI machines, surgical robots, and patient monitoring systems, people commonly use displacement transducers.
Conclusion
Displacement transducers are crucial in many industries, offering accurate and reliable measurement of position and movement. Whether you’re in the automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, or medical field, understanding displacement transducer design and services can help you choose the right solution for your needs. With proper calibration, maintenance, and integration, these devices can significantly enhance the performance and accuracy of your systems.
If you’re looking to implement displacement transducers in your operations or need expert advice, specialized service providers can guide you through the process, from design to integration and beyond.
contact us
For greater statistics about our Displacement Transducer about your unique assignment desires, please touch us:
Office Address: Office # 9, First floor, Business Incubation Center SSC, University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore.
Phone: +923234767694
Email: info@etazsystems.Com
At eTAZ Systems, we are devoted to turning in innovative and reliable Displacement Transducer services that pressure the achievement of our customers’ projects. Reach out to us these days to look how we are able to assist carry your electronic designs to lifestyles.
Pingback: CB CAD Design: 3D Design Top View | eTAZ Systems -