Hall Effect transducers are crucial components in many industries, especially when it comes to measuring magnetic fields or current sensing. These transducers work based on the Hall Effect, a principle discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879, which allows for the conversion of a magnetic field into an electrical signal. eTAZ systems Moreover view explores the design, applications, benefits, and frequently asked questions about Hall Effect transducers, providing a clear understanding of how they work and where they are used.
What is a Hall Effect Transducer
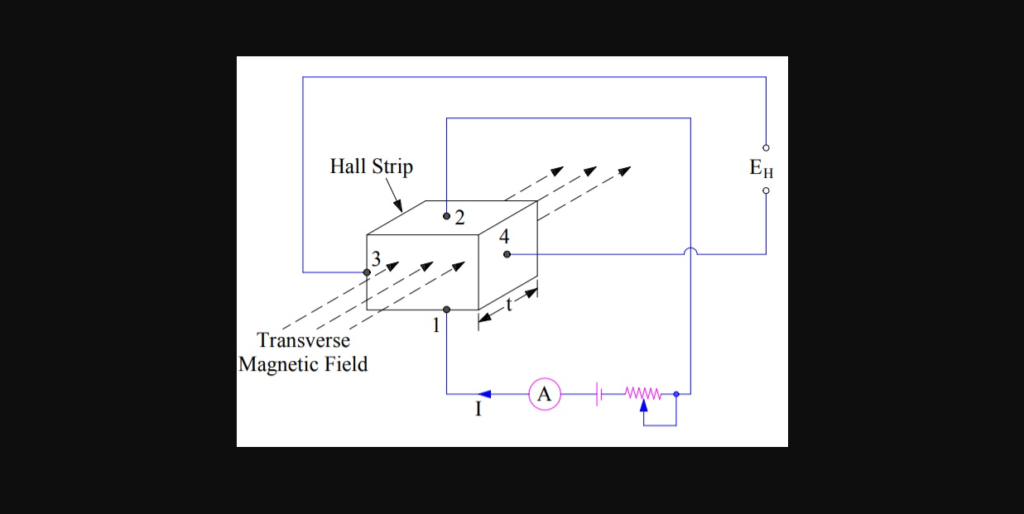
A Hall Effect transducer is a device that generates a voltage output that corresponds to the intensity of a magnetic field. The Hall Effect occurs when a voltage (called Hall voltage) is produced perpendicular to the current flow in a conductor that is exposed to a magnetic field. Hall Effect transducers utilize this phenomenon to measure magnetic fields or currents without needing direct electrical contact, making them useful for a variety of applications.
Design and Working Principle of Hall Effect Transducers
Hall Effect transducers typically include the following components:
Hall Element: This is a thin semiconductor material, often made from gallium arsenide (GaAs) or indium antimonide (InSb). When a current flows through this element and it encounters a magnetic field, a voltage is generated across its width—this is the Hall voltage.
Magnetic Field Source: This can be an external magnetic field or one generated by current-carrying conductors. The strength and direction of this field affect the magnitude and polarity of the Hall voltage.
Signal Conditioning Circuit: The Hall voltage generated is usually small, so it needs to be amplified and filtered. This is where the signal conditioning circuit comes in, making the output usable for further processing or display.
Housing and Mounting: Hall Effect transducers are housed in protective enclosures to shield them from environmental factors. They are also designed for easy installation in different setups.
Working Principle
When a conductor carrying a current is placed in a magnetic field perpendicular to the current flow, the charge carriers (electrons or holes) in the conductor experience a force that pushes them to one side. This creates a voltage difference across the conductor, known as the Hall voltage. Therefore strength of this voltage depends directly on the magnetic field’s intensity and the current flowing through the conductor.
Applications of Hall Effect Transducers
Hall Effect transducers are widely used across various industries due to their versatility, ability to measure without contact, and high accuracy. Some of their common applications include:
Current Sensing:
Automotive Industry: Used to monitor current in electric vehicle motors, battery systems, and charging circuits.
Power Electronics: Employed in inverters, nevertheless otor drives, and power supplies to provide feedback on current levels.
Position Sensing:
Rotary Encoders: Detect the position of rotating shafts in industrial automation.
Linear Position Sensors: Determine the linear position of components in robotics and manufacturing.
Speed Detection:
Wheel Speed Sensors: Measure the rotational speed of wheels in anti-lock braking systems (ABS) in vehicles.
Tachometers: Measure motor speeds in various industrial applications.
Proximity Detection:
Magnetic Proximity Sensors: Common in security systems, hence door sensors, and safety interlocks.
Magnetic Field Sensing:
Gaussmeters: Instruments that measure the strength and direction of magnetic fields in labs and industrial settings.
Benefits of Hall Effect Transducers
Hall Effect transducers come with several advantages, making them a popular choice in many applications:
Non-Contact Measurement: They measure magnetic fields without needing direct contact, which reduces wear and tear.
High Accuracy: They offer precise measurements of magnetic fields and currents, which is vital in motor control and battery management.
Wide Operating Range: These transducers work well across a broad range of temperatures and magnetic field strengths, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Low Power Consumption: Many Hall Effect transducers consume minimal power, making them ideal for battery-powered devices.
Versatility: They can measure magnetic fields in different ways, additionally allowing them to be used in various applications.
Compact Size: Their small size allows for easy integration into tight spaces and complex systems.
Hall Effect Transducer Services by eTAZ Systems
At eTAZ Systems, we offer a wide range of Hall Effect transducer services tailored to meet the needs of various industries. Our services include:
Custom Design and Development: We design and develop Hall Effect transducers to meet specific application requirements, whether for current sensing, position detection, or speed measurement.
Calibration and Testing: We provide precise calibration and testing to ensure optimal performance. Our facilities are equipped to handle various testing scenarios.
Integration Support: We offer support for integrating Hall Effect transducers into your existing systems, including advice on mounting, wiring, and interfacing.
Maintenance and Repair: We provide maintenance and repair services to keep your Hall Effect transducers running smoothly and efficiently.
Training and Consultation: We offer training on proper usage and maintenance, as well as consultation to help you select the right transducer for your application.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the Hall Effect?
The Hall Effect is the generation of a voltage across a conductor carrying a current when placed in a magnetic field. This voltage is directly proportional to the magnetic field’s strength and the current.
Q2: How does a Hall Effect transducer work?
A Hall Effect transducer uses the Hall Effect principle to generate a voltage perpendicular to the current flow when exposed to a magnetic field. This voltage is then processed to produce a usable output signal.
Q3: What are the main applications of Hall Effect transducers?
They are commonly used in current sensing, position sensing, speed detection, proximity detection, and magnetic field sensing across industries like automotive, industrial automation, and security systems.
Q4: What are the advantages of using Hall Effect transducers?
These include non-contact measurement, high accuracy, wide operating range, low power consumption, versatility, and compact size.
Q5: Can Hall Effect transducers measure both AC and DC currents?
Yes, they can measure both AC and DC currents, making them versatile for different applications.
Q6: What factors should be considered when selecting a Hall Effect transducer?
Consider factors such as sensitivity, operating temperature range, power consumption, size, and the specific application requirements.
Q7: How often should Hall Effect transducers be calibrated?
Generally, they should be calibrated annually or whenever subjected to extreme conditions.
Q8: Can Hall Effect transducers be used in harsh environments?
Yes, they can be designed to operate in harsh environments and are available in rugged housings to protect them from dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Q9: How can I integrate a Hall Effect transducer into my system?
Proper mounting, wiring, and interfacing with other components are crucial. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional assistance.
Conclusion
Hall Effect transducers are essential in modern technology, providing accurate and reliable measurements of magnetic fields and currents across various applications. eTAZ Systems is committed to offering top-notch Hall Effect transducer services, Furthermore ensuring efficient and effective operation of your systems. Whether you need custom design, calibration, integration support, or maintenance, our team is ready to assist you.
For more information on our Hall Effect transducer services or to discuss your specific requirements, please contact us at eTAZ Systems. We’re here to help you find the perfect solution for your needs.
contact us
Furthermore greater statistics about our Hall Effect Transducer about your unique assignment desires, please touch us:
Office Address: Office # 9, First floor, Business Incubation Center SSC, University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore.
Phone: +923234767694
Email: info@etazsystems.Com
At eTAZ Systems, we are devoted to turning in innovative and reliable Hall Effect Transducer Services that pressure the achievement of our customers’ projects. Reach out to us these days to look how we are able to assist carry your electronic designs to lifestyles.
Pingback: CB CAD Design: 3D Design Top View | eTAZ Systems -
Pingback: Explore How AC and DC Power Differ -